Facilities Management
Central Utility Plant
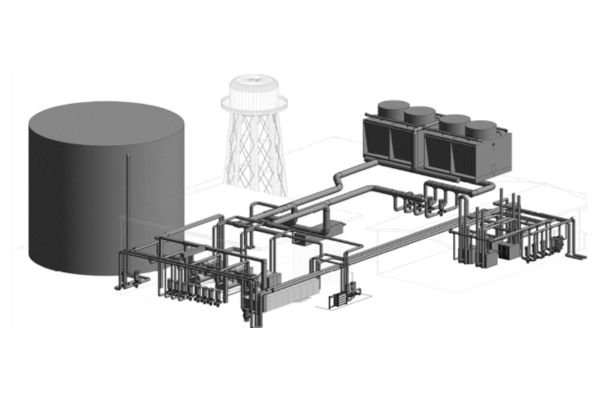
The Fresno State Central Utility Plant (CUP) is comprised of a boiler plant, chiller plant, thermal energy storage (TES) tank, cooling tower, and related components and provides centralized heating and cooling to campus buildings. The original boiler and chiller plants built in the 1950s and upgraded in the 1990s, worked independently of each other, using separate utilities and often working against each other by simultaneously heating and cooling buildings on campus. The Central Utility Plant Replacement (CUPR) project replaced and upgraded various equipment, connecting components of the CUP, allowing the plants to communicate and work together while realizing greater efficiencies. The new CUP uses 73% less natural gas than the original equipment.
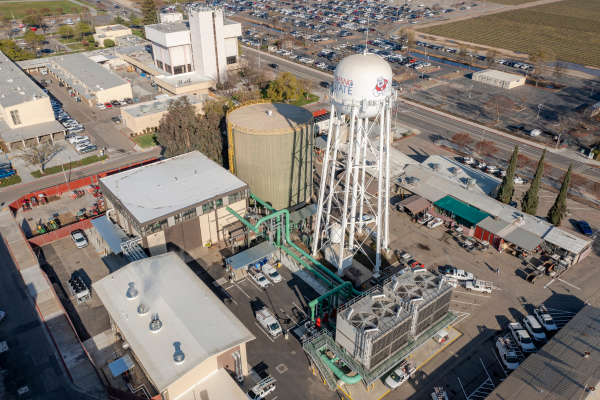

Chiller Plant
Fresno State’s chiller plant is a centralized cooling system that produces a low-temperature fluid which is circulated throughout campus to provide cooling to buildings. Chillers are among the largest consumers of energy in a building. The upgraded chiller plant includes these features:
- Centralized plant with 3,700 tons of cooling capacity
- Three 1,000-ton high efficiency variable-speed centrifugal chillers
- One 700-ton modular heat recovery chiller
- Upgraded and reused existing cooling tower
- Upgraded/refurbished existing thermal energy storage (TES) tank
- Refurbished existing chiller plant building
Before
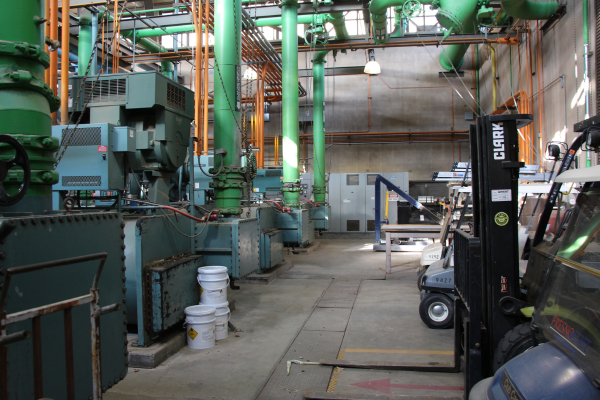

Front view of the original chillers
After
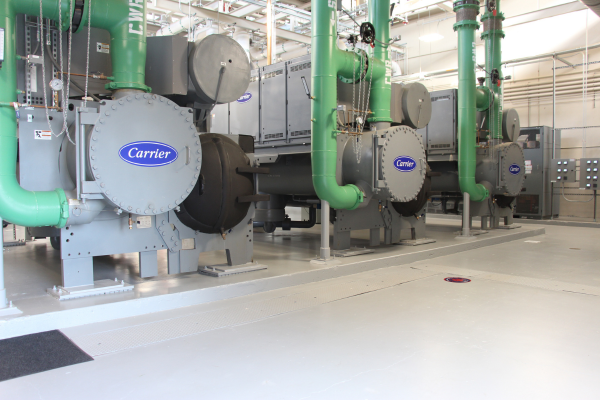

Front view of the new variable-speed centrifugal chillers
Before
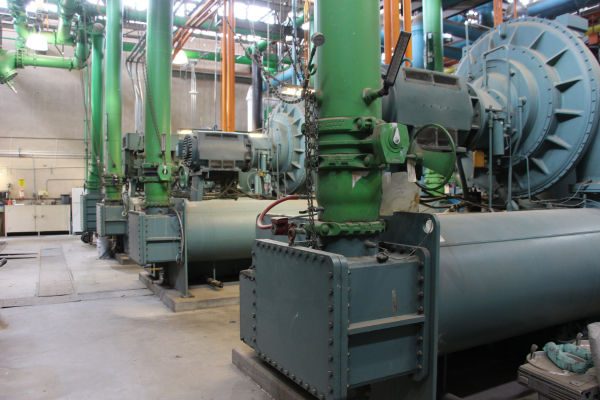

Back view of the original chillers
After
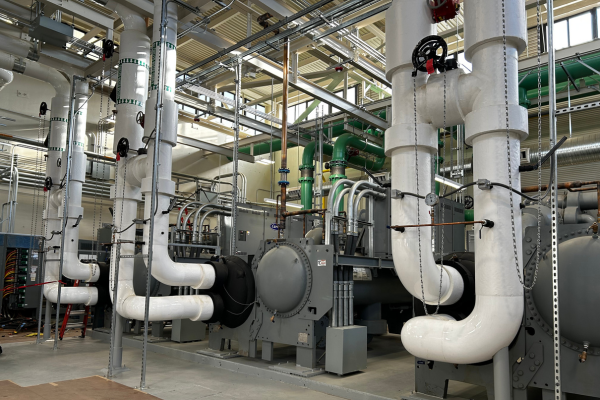

Back view of the new variable-speed centrifugal chillers
Before
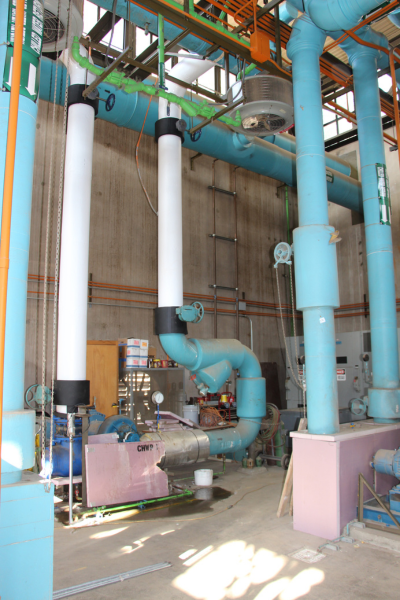

Original chilled water pumps
After
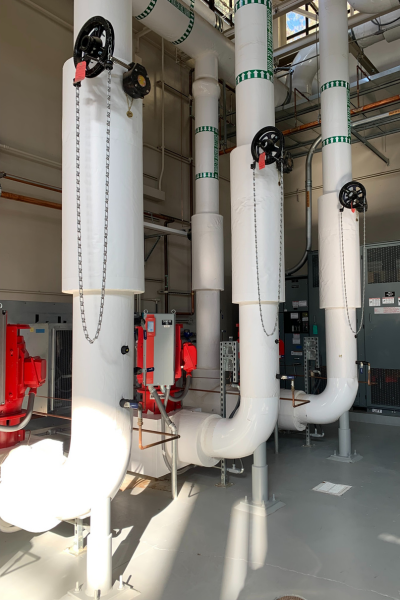

New chilled water pumps
Before
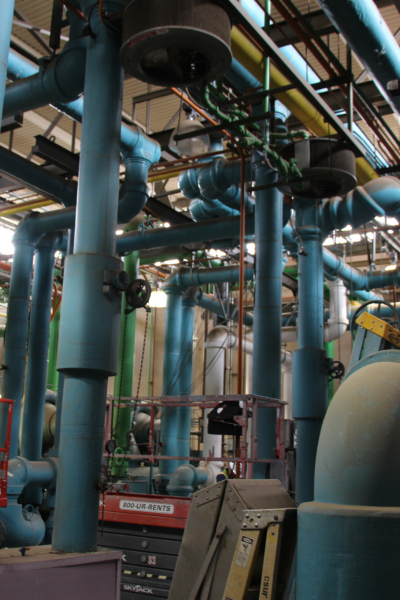

Original chiller plant piping
After
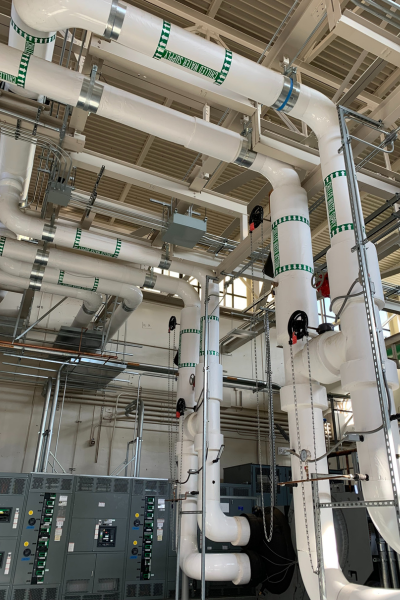

New chiller plant piping
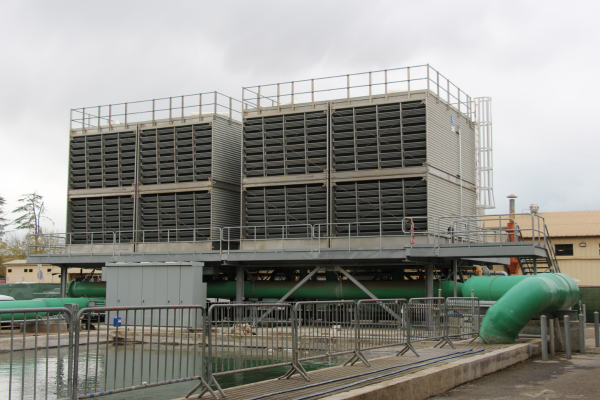
Cooling Tower
The cooling tower (also known as the condenser) is a major component of the chiller plant. The cooling tower releases waste heat extracted from buildings through a waterfall-like effect. This allows the air to cool the water which in turn, removes heat from the refrigerant. When construction started for the new CUPR project, this condenser was only three years old so it was upgraded and refurbished for connection to the CUP.
Before
Cooling tower before refurbishment.
After
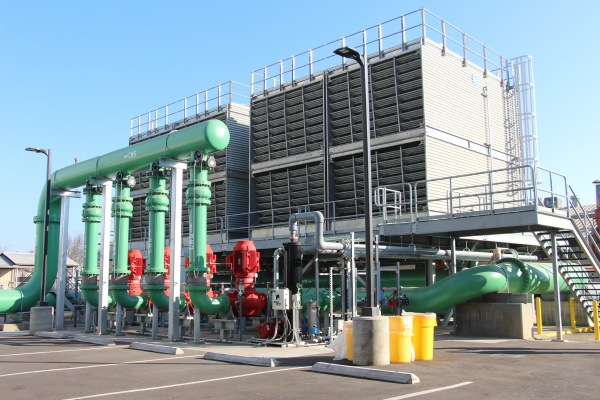

Cooling tower after refurbishment.
Thermal Energy Storage (TES) Tank
The thermal energy storage (TES) tank is another major component of the chiller plant. This tank is a million-gallon, slow moving accumulation of water. The cold water in the tank is used during the day to offset the chiller usage and cool campus buildings. Warmed water comes back to the tank from campus buildings through newly installed underground distribution pipes. At times of peak energy cost, the TES tank allows the chiller plant to avoid mechanical cooling by pulling cool water from the bottom and returning hot water to the top. As part of the CUPR project, the tank interior was sandblasted clean and connected to the chilled water loop. The exterior of the tank was also cleaned.
Before
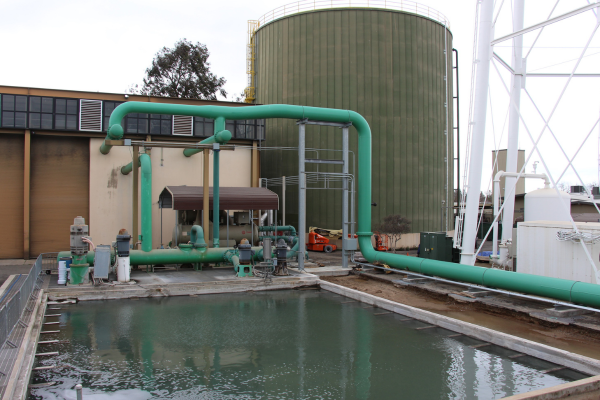

TES tank before the exterior was cleaned and interior sandblasted.
After
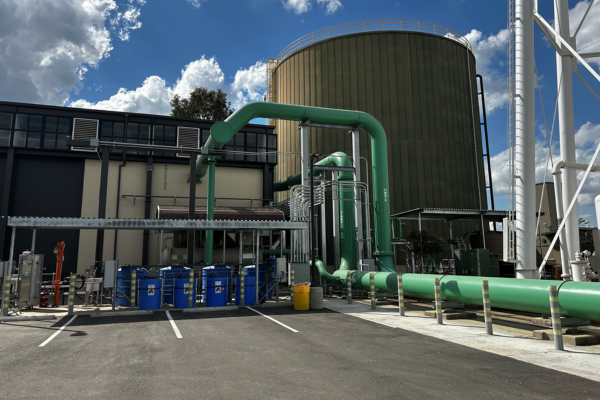

TES tank after the exterior cleaning and interior sandblasting.
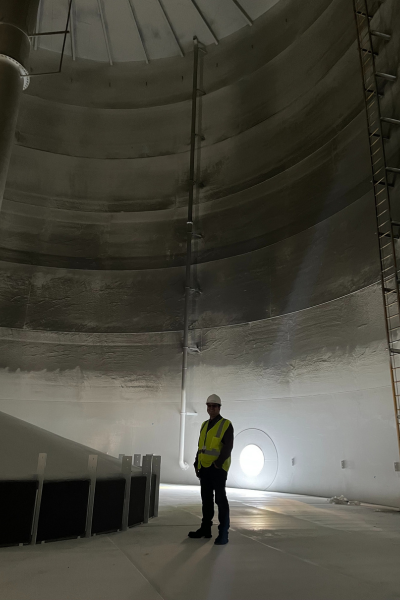

A BIG construction team member demonstrates scale inside the million-gallon tank.
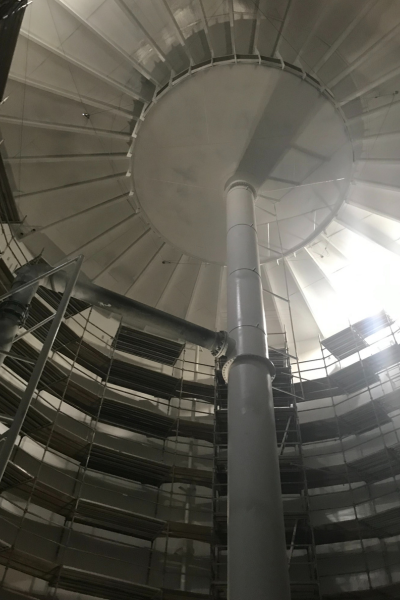

Scaffolding enabled the team to sandblast the interior.
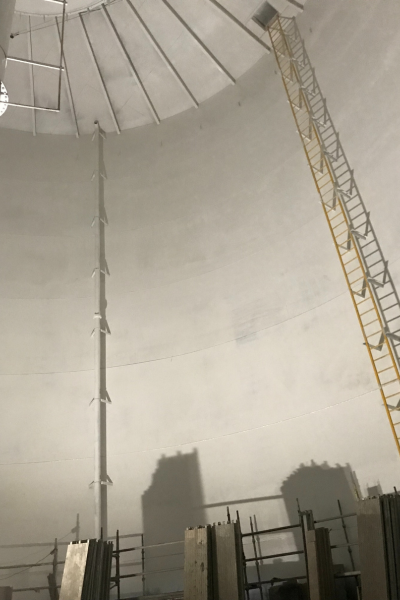

The interior of the TES tank after sandblasting.
Water Tower

Fresno State’s boiler plant is centrally located to campus buildings and creates thermal energy in the form of hot water to supply to campus. Seven new modular condensing boilers with digital controls were installed in 2023 to replace the three original boilers. The original boilers were so big that a single boiler took up the entire space of the concrete pad that four of the new boilers now occupy. The new boilers feature upgraded digital controls that provide improved monitoring and temperature control. The upgraded boiler plant includes:
- 46,100 MBH of total heating capacity
- Seven modular condensing boilers (combined with modular heat recovery chiller located in the chiller plant)
- Refurbished existing boiler plant building with added office space
Before
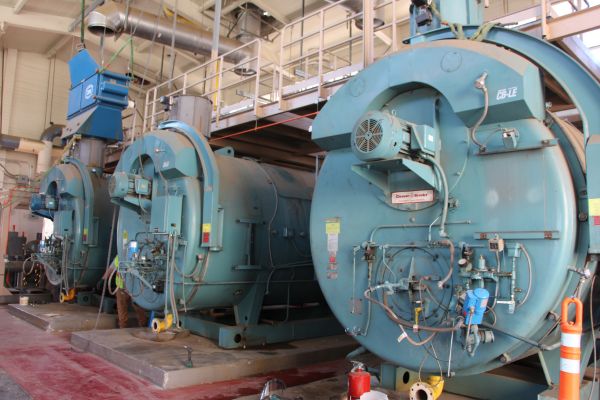

Original pneumatic boilers
After
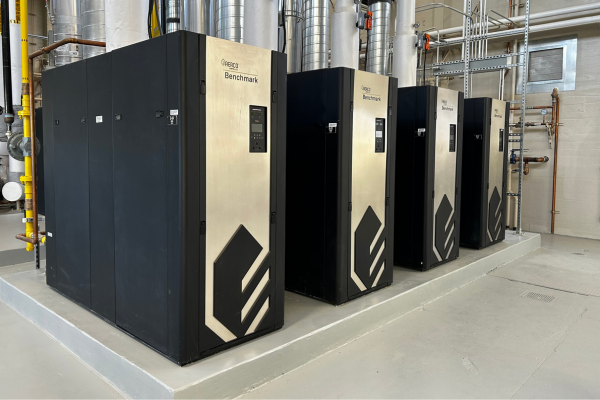

New modular condensing boilers